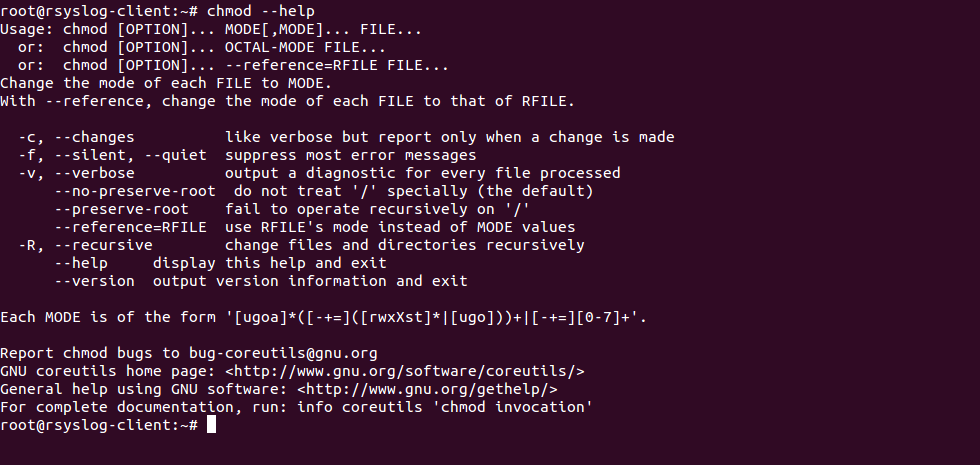
Change ** to the type of files you would like to change its permissions ** will apply the changes to all files in the directory Share Improve this answer To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following chmod rwx filename to add permissions chmod rwx directoryname to remove permissions chmod x filename to allow executable permissions chmod command is used to change access permission of files and directories in Linux operating systems chmod stands for change mode Access permissions specify whether a user account or group can read, write, or execute a given file and directory

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut
Chmod command in linux for directory
Chmod command in linux for directory-In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals SETUID AND SETGID BITS top chmod clears the setgroupID bit of a regular file if the file's group ID does not match the user's effective group ID or one of the user's supplementary group IDs, unless the user has appropriate privileges Combining the find command with chmod can also be used for changing the permission of files that are a specific type The command syntax for changing the permission of a specific file type in a directory is find directory name "* filename_extension"




Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium
1026 If you are going for a console command it would be chmod R 777 /www/store The R (or recursive) options make it recursive Or if you want to make all the files in the current directory have all permissions type chmod R 777 / If you need more info about chmod command see File permission Share Linux File Permission chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure soThe Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;
A and b will be created with the default permission from your umask Instead to create any new directories with permission 777, run mkdir p in a subshell where you override the umask (umask u=rwx,g=rwx,o=rwx && mkdir p a/b/c) Note that this won't change the permissions if In Linux, access to the files is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directories This tutorial covers how to use the chmod command 1 Answer1 Active Oldest Votes 1 find and chmod find path_to_dir type f name "**" exec chmod 775 {} \;
chmod = Change mod chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file and directory Linux and Unix operating systems provide the chmod command in order to change access permission for the files and folders The chmod command name comes from change mode The read, write, execute permissions with the sticky First, open terminal Then use the cd command to go to the directory where the file you want edit is Now use the following command to see the permission granted to the file Ls –l filename Now you just need to use the attributes explained above Use the following example to execute the chmod command in Linux




Chmod Cheatsheet Linux



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders
I have no idea how I could miss something so simple for so many years The more I learn theThe chmod 755 is often used as the R 755 in the Linux shell to modify the filesystem's permission You can run the chmod 775 commands on your Linux terminal shell if you cant write or remove files from any directory The chmod R 775 command has the power to change the permission for an entire directory instead of a single file The following screenshot shows the execution of the command on a Linux Environment The command executed here is chmod 777 R home and it gives 777 permission to the folder home itself, also to all of the files and subdirectories inside this folder The format of the command is chmod XXX R directorylocation You might also require to run




What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize




Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the R, (recursive) option The general syntax to recursively change the file's permissions is as follows chmod R MODE DIRECTORYRunning openbox here but you can do this in just about any environment how you define the hotkey is gonna be specific to your window manager, though I have four Linux machines here to manage, this is what it looks like in ~/config/openbox/rcxml;10 rows The find command will search for files and directories under /var/www/my_website and pass each




Unix Permissions




How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Don't do mkdir m 777 p a/b/c since that will only set permission 777 on the last directory, c; Using Options with chmod and chown Commands Option is an additional command to change the output of a command One of the most popular options that you can combine with chmod and chown is R (Recursive) This Linux option allows you to change permissions or owners of all files and subdirectories inside a specific directoryTo use chmod, you need to know about access modes Each file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determine
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change



3
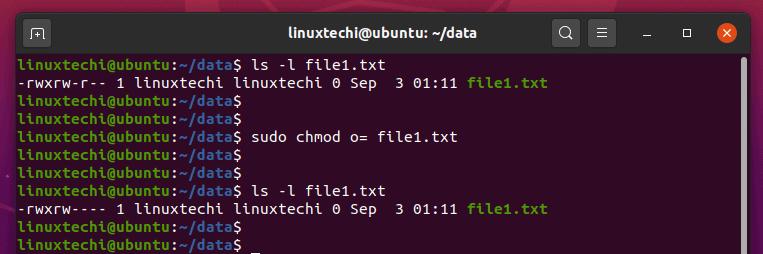
The Linux command to change permissions on a file or directory is chmod, which we like to read as change file mode chmod has two operating modes symbolic mode;Chmod means 'change mode' and it changes file or directory mode bits (the way a file can be accessed) You can use chmod in the command line to change file or directory permissions on unix or unixlike systems such as linux or BSD Changing File or Folder permissions with 'chmod' command Change mode is shortly known as chmod you can change the permissions like ( read, write, execute) on your file or folder for the owner and group Based on the following syntax you change the file permission chmod permissions filename




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change mode This article explores chmod 777, a Linux command used to give ALL RIGHTS to the user, group, and others As a new Linux user, web developer, or system administrator, you have probably been instructed to type chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder into your Linux shell at some point Whenever you're running commands on your systems (especially as root!), you should As you might remember, the default file permission value is 0644, and the default directory's is 0755 The default umask value is subtracted from the overall file/directory default value You can set the umask values in /etc/profile or in ~/bashrc Wrapping up Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Open Terminal from the Applications folder or using Spotlight At the command prompt, navigate to the directory that contains the item (s) you want to edit For example cd Documents/Work Type the command ls l to view (in long format) the contents of the folder and each item's permissions chmod – adds and removes permissionsIf you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks ch'mod How does chmod work?Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium
R Reading access/view file Users can read file In other words, they can run the ls command to list contents of the folder/directory w Writing access/update/remove file Users can update, write and delete a file from the directory x Execution access Run a file/script as command Users can execute/run file as command and they The chmod command allows users to change read and write permissions in Unix systems In this guide, we will show you how to modify file and directory permissions with chmodAfter changing a directory's mode to 750 the folder's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as d rwxrx Popular CHMOD Commands (TOP ) chmod 777




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
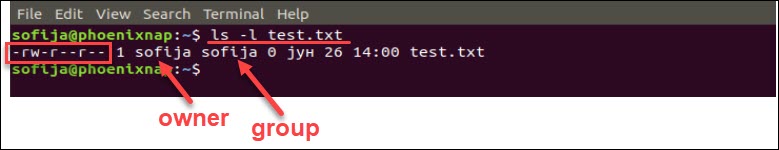
Ll Directory Name chmod OPTION Access Type Directory Name/Path chown OPTION Owner/Group Directory Name/Path ll The "ll" command is useful to print the directory permission information of the specific directory chmod We can use the chmod keyword in the syntax or command It will take the two arguments as access permission and the directoryTo put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users rwrr 1 john john 272 Mar 17 02 testtxt In the above example User (john) has read and write permissionTo change permission using the Linux chmod command we have to follow some syntax and rules




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube




Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory
Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command The basic syntax is chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission using symbols (alphanumerical characters) chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions There are three sets of permissions One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file's group, and a final set for everyone else The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory In Linux, file and directory permissions can be modified in two different ways using the chmod command with symbolic format or with numeric format
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/create-directories-linux-mkdir-command-3991847-55ea75a52f7842a2af0fdfe0b7470270.gif)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux



Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com
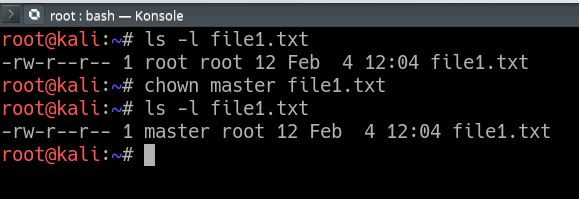
The command CHMOD stands for change mode, and this is used to change the permission of a File or Directory The Command CHOWN stands for Change Owner and this is used to change the ownership of a File or Directory Also Read Linux Tutorial for Beginners && Git Tutorial for Beginners Let us understand CHMOD and CHOWN commands in detail




Perl Chmod Command How To Set And Remove File And Directory Permissions Udemy Blog




Uajddgnsbm2com




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions



Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




File Chmod Gnu Png Wikipedia




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu




Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)



Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
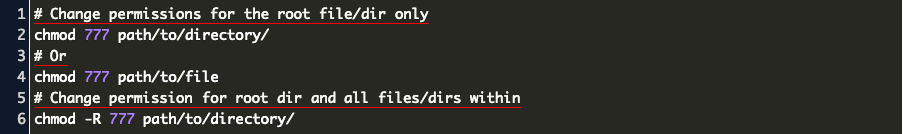



Give Full Permission To Folder And Subfolders In Linux Code Example
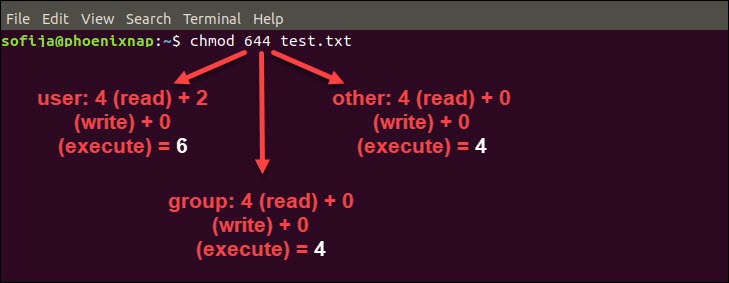



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
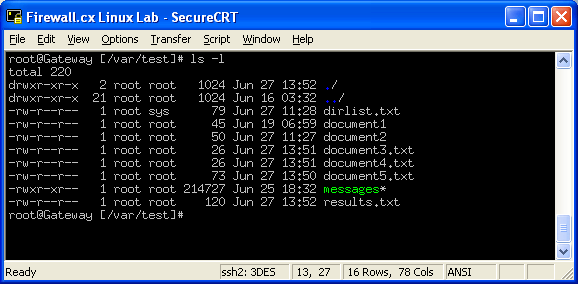



Linux File Folder Permissions



1
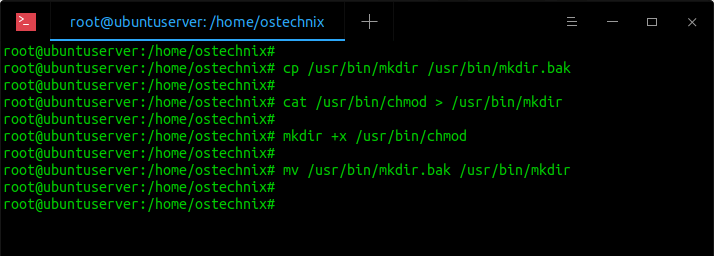



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
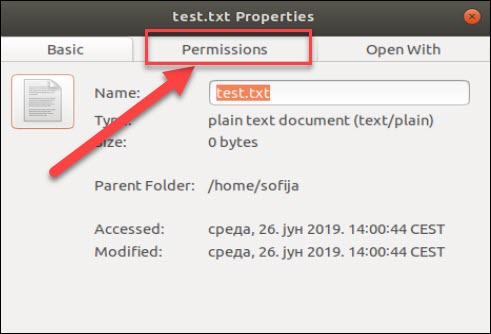



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
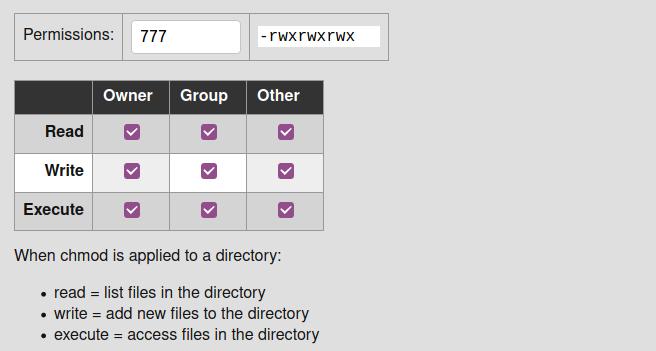



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



1




08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube




How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight




Ownership And Permissions
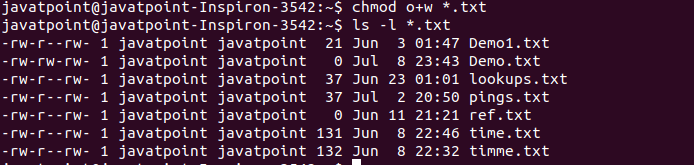



Linux Chmod Command Javatpoint




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff




Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
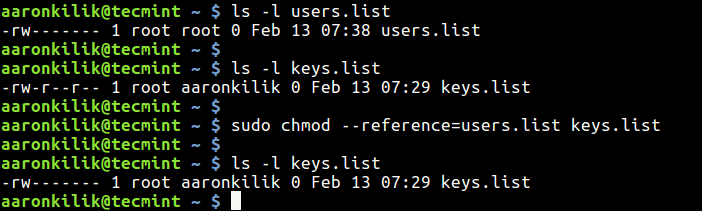



How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux Commands Chmod




Linux File Permission Javatpoint
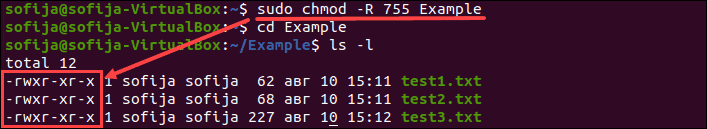



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




Introduction To The Linux Chmod Command Opensource Com



Linux Command Line Basics Part 4 I Have A Pc I Have A Pc




Linux Users And Groups Linode



Common Bash Commands
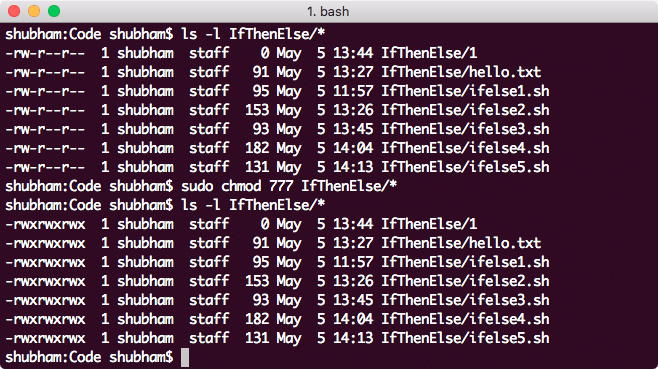



Linux Chmod Example



Linux Unix File Permissions




Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu
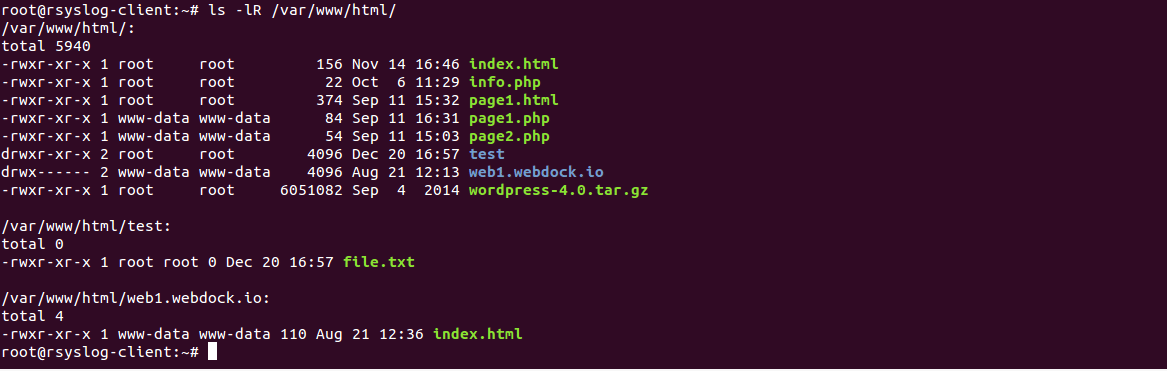



Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders




Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets




Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples It Smart Tricks




Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix
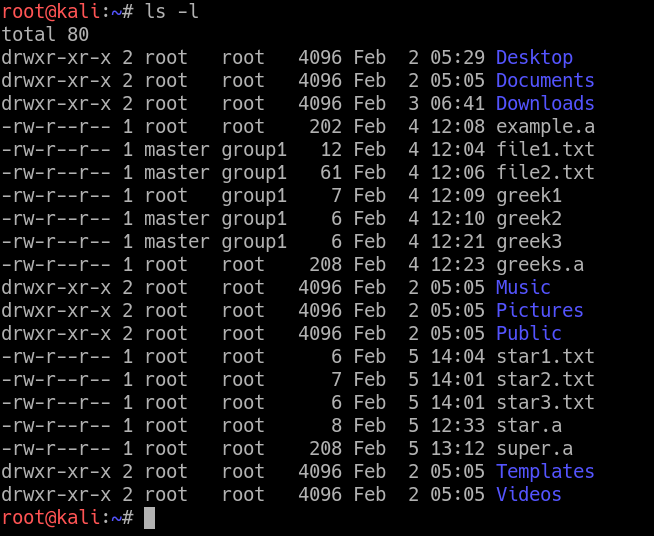



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod How To Set File And Directory Permission In Linux Using Chmod Youtube




Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog




Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau




Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
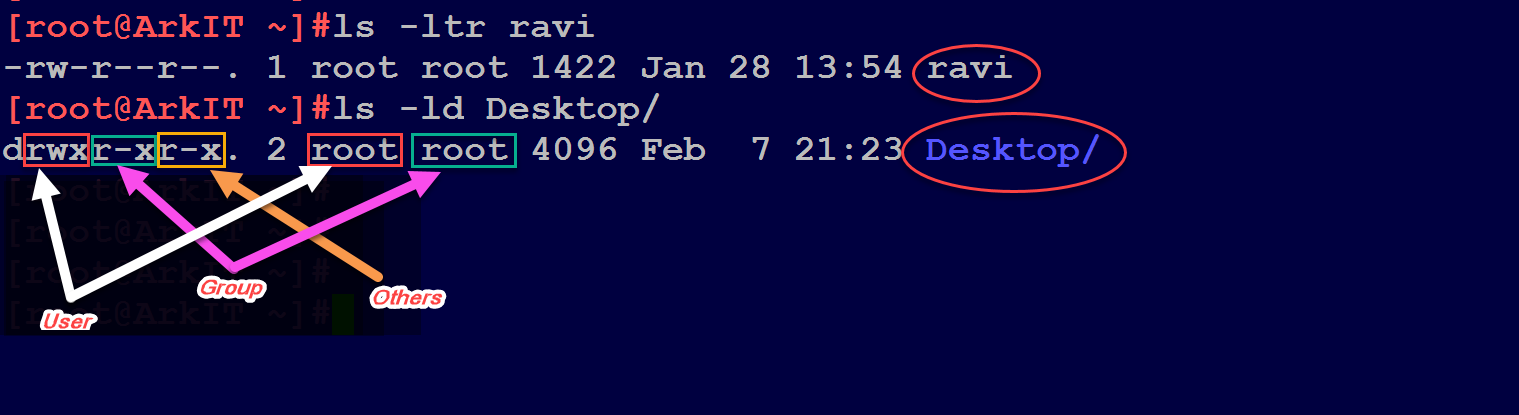



Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions
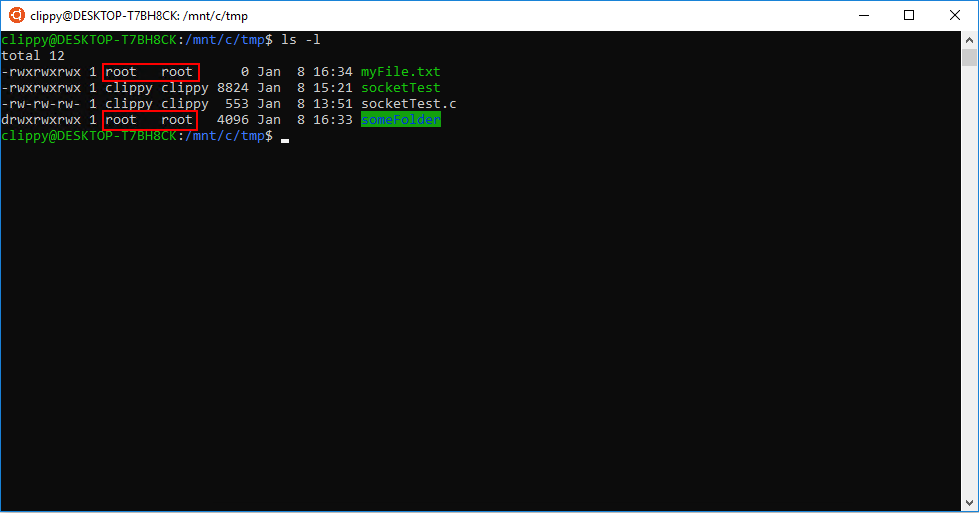



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube
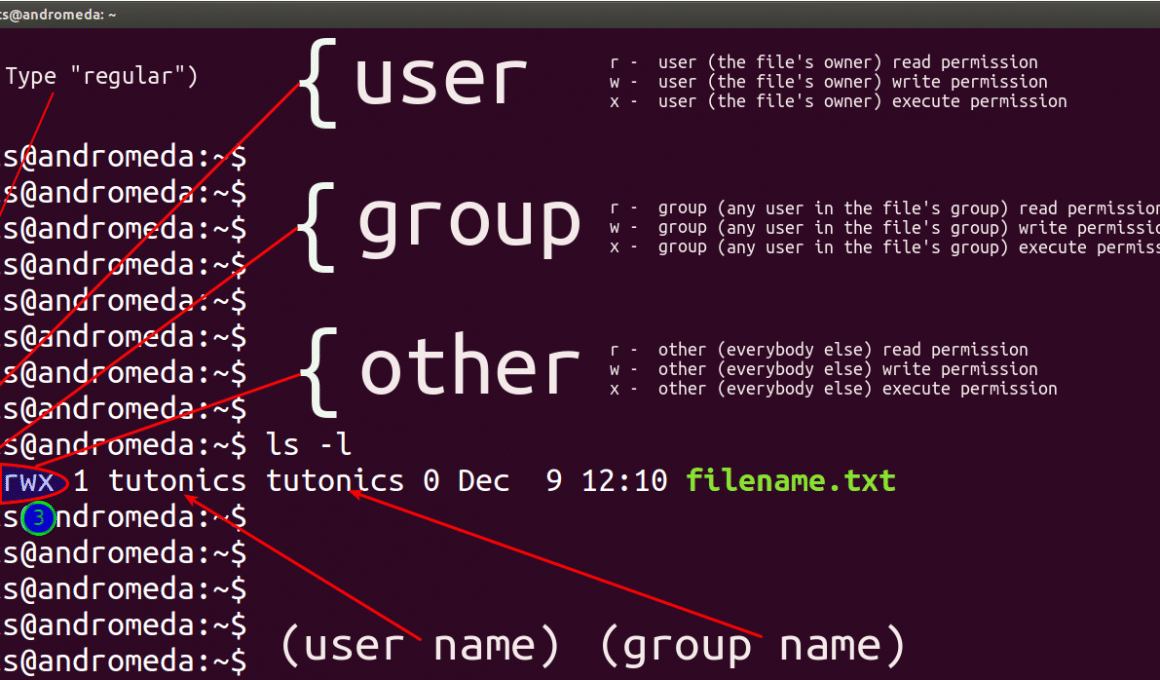



Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/mkdir-linux-5c4763ffc9e77c00014ae996.png)



How To Create Directories In Linux With The Mkdir Command
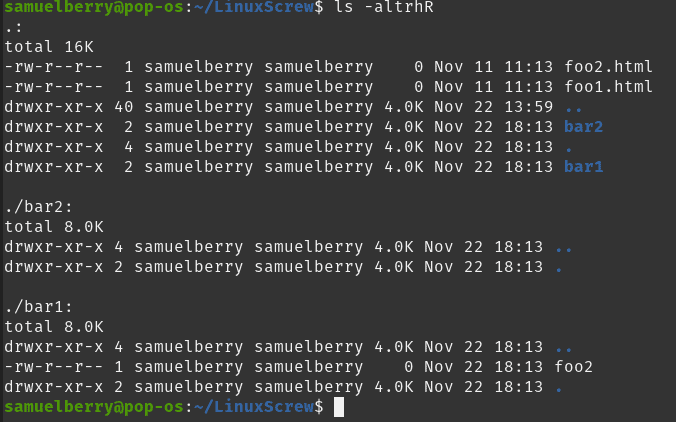



Linux Chmod Recursive How To Change File Permissions Recursively




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
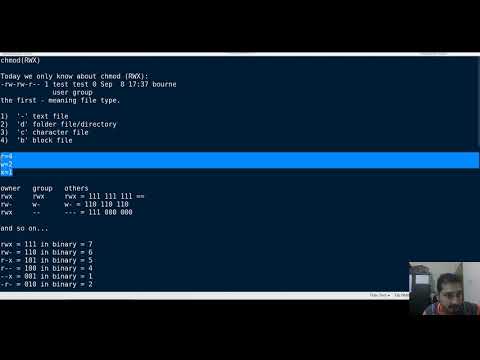



How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux Basic Linux Permission Linux File Permission Wiz Maverick Benisnous




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
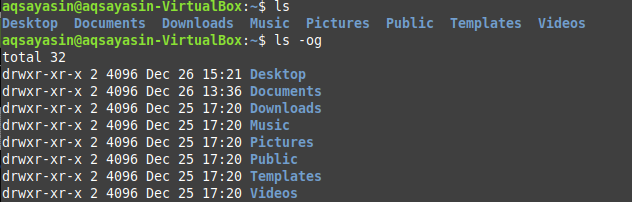



Linux Chmod Command Tutorial For Beginners




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
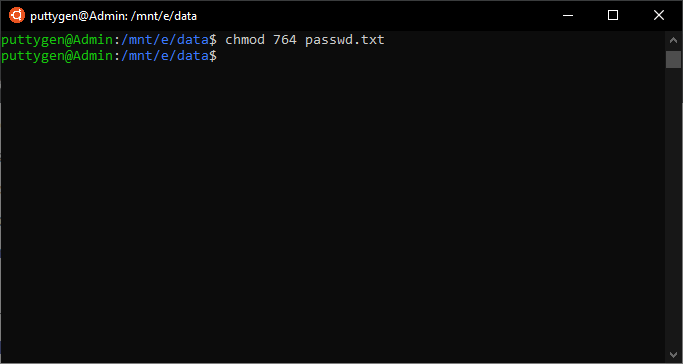



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿